2020-06-22
Shanghai: 2692 tumor patients received proton heavy ion therapy in 5 years, 94.4% did not undergo surgery
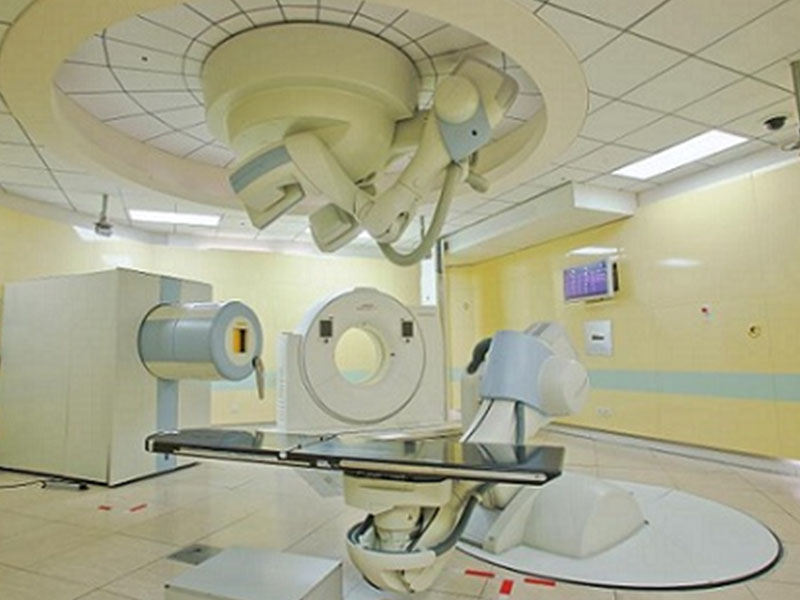
China Youth Daily, Shanghai, May 8th (China Youth Daily, China Youth Network reporter Wang Yejie) Today, reporters learned from Shanghai Proton Heavy Ion Hospital that in the past five years of its opening, the hospital has treated 2692 patients and discharged them. Among them, 2542 patients were treated solely with heavy ions or heavy ion combined proton therapy, accounting for 94.4% of the total.
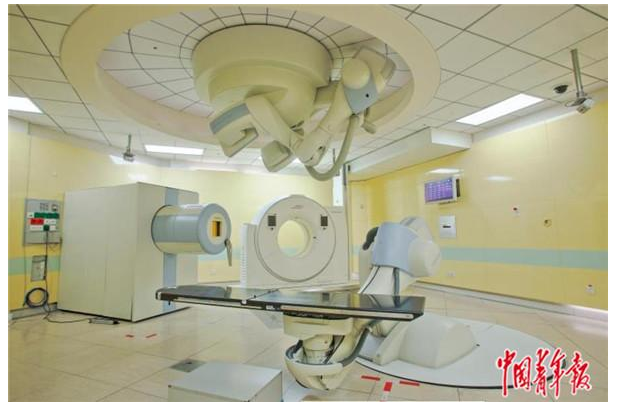
Proton and heavy ion technology is one of the radiation therapy technologies and is internationally recognized as a cutting-edge technology in radiation therapy. Protons and heavy ions both belong to particle lines, which, unlike traditional photon lines, can form energy Bragg peaks, reducing damage to human health tissues while centrally exploding tumors.
The reporter from Zhongqing Daily and Zhongqing Net noticed that there is still controversy over the early promotion and use of proton heavy ion technology in China. At that time, its equipment was expensive, its efficacy was not yet clear, and the reserve of doctors skilled in operating the technology was insufficient. But over the past five years, its efficacy in the treatment of some tumors has been relatively clear.
In recent five years, the hospital has carried out clinical treatment around five key diseases with high incidence rate in China, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma, intracranial skull base tumor, early lung cancer, liver cancer, prostate cancer, and carried out key clinical research on pancreatic cancer ("5+1" key diseases). The hospital's first standardized heavy ion radiotherapy for locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma has become an internationally recognized standard in the field of particle radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Heavy ion radiotherapy for medium to high-risk prostate cancer can improve patient survival rate and quality of life.
The clinical treatment of intracranial skull base tumors is quite challenging. The hospital used simple heavy ions or heavy ions combined with proton therapy to treat 137 cases of chordoma and chondrosarcoma. The overall 2-year survival rate of the patients was 88.4%, and the 2-year local tumor control rate was 88.1%. There were no serious acute or late adverse reactions.
The hospital has treated 113 locally advanced or refused surgery cases of liver cancer. Among them, 50 cases (with a median tumor diameter of 5.1cm) were treated with 10 doses of heavy ion irradiation, resulting in a 3-year overall survival rate of 72% and a 3-year local tumor control rate of 85%. The therapeutic effect is close to surgical treatment.
In addition, the hospital has initiated and published a guideline monograph on proton heavy ion therapy, providing specific clinical treatment practices for peers worldwide.
In terms of talent cultivation for proton and heavy ion shortage, the hospital has relied on Fudan University for 5 years to create and continuously cultivate 6 batches of 52 master's degrees in radiation physics, biomedical engineering, and has successfully graduated from 4 batches of 35 people. It has provided core professional talents for similar medical institutions and research and development institutions under construction or preparation in China. In January of this year, the hospital was officially listed as an affiliated hospital of Fudan University. With the strong support of Fudan University's medical teaching and research resources, talent cultivation has been further accelerated. At present, a first generation "localized" core talent team for particle radiation physics and radiation therapy with a reasonable structure has been preliminarily established.